ModelRenderer
- The Model Renderer is the component responsible for rendering models of your scene, whether 3D or not, it is also responsible for manipulating its respective Material. To deform models for use in bone animations, use SkinnedModelRenderer.
Properties
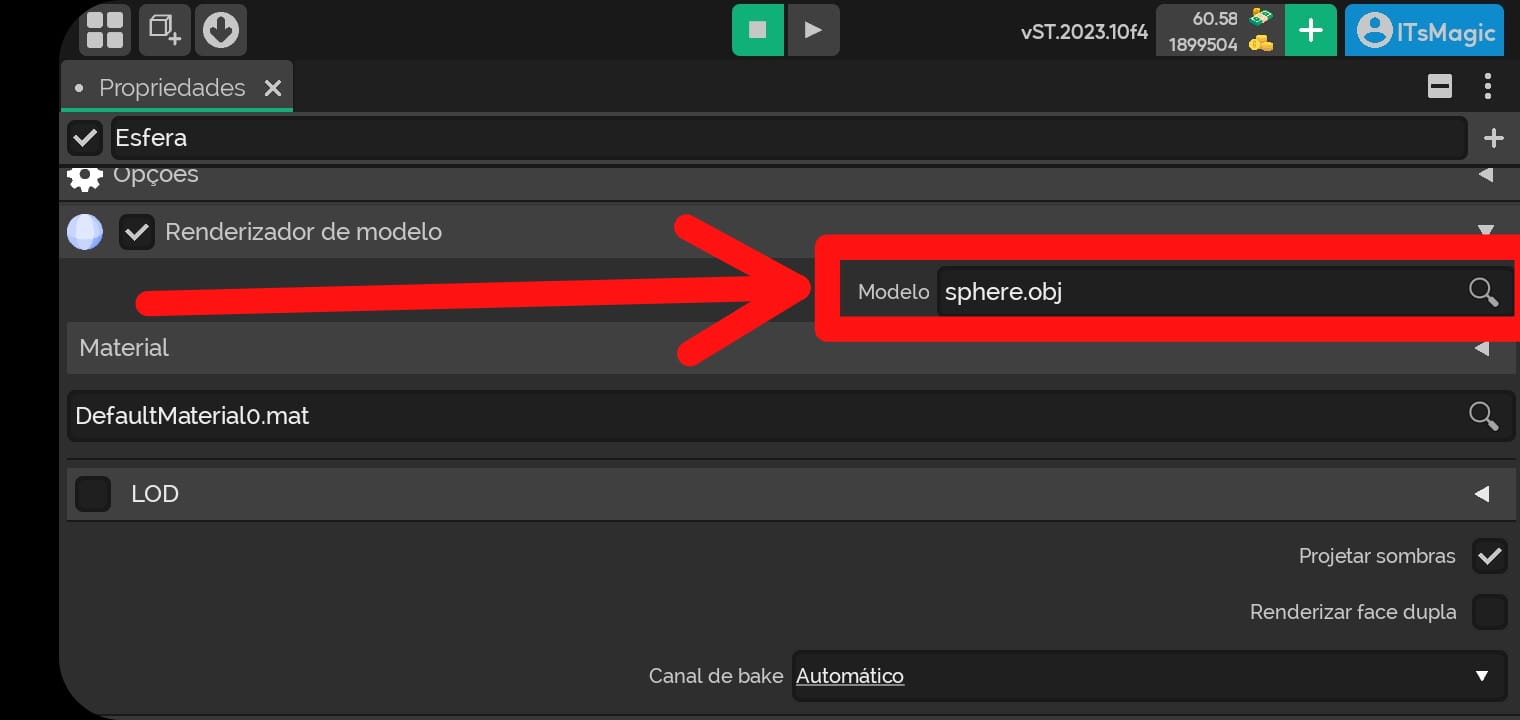
Model
- The model (3D or 2D) that the model renderer will render in the scene.
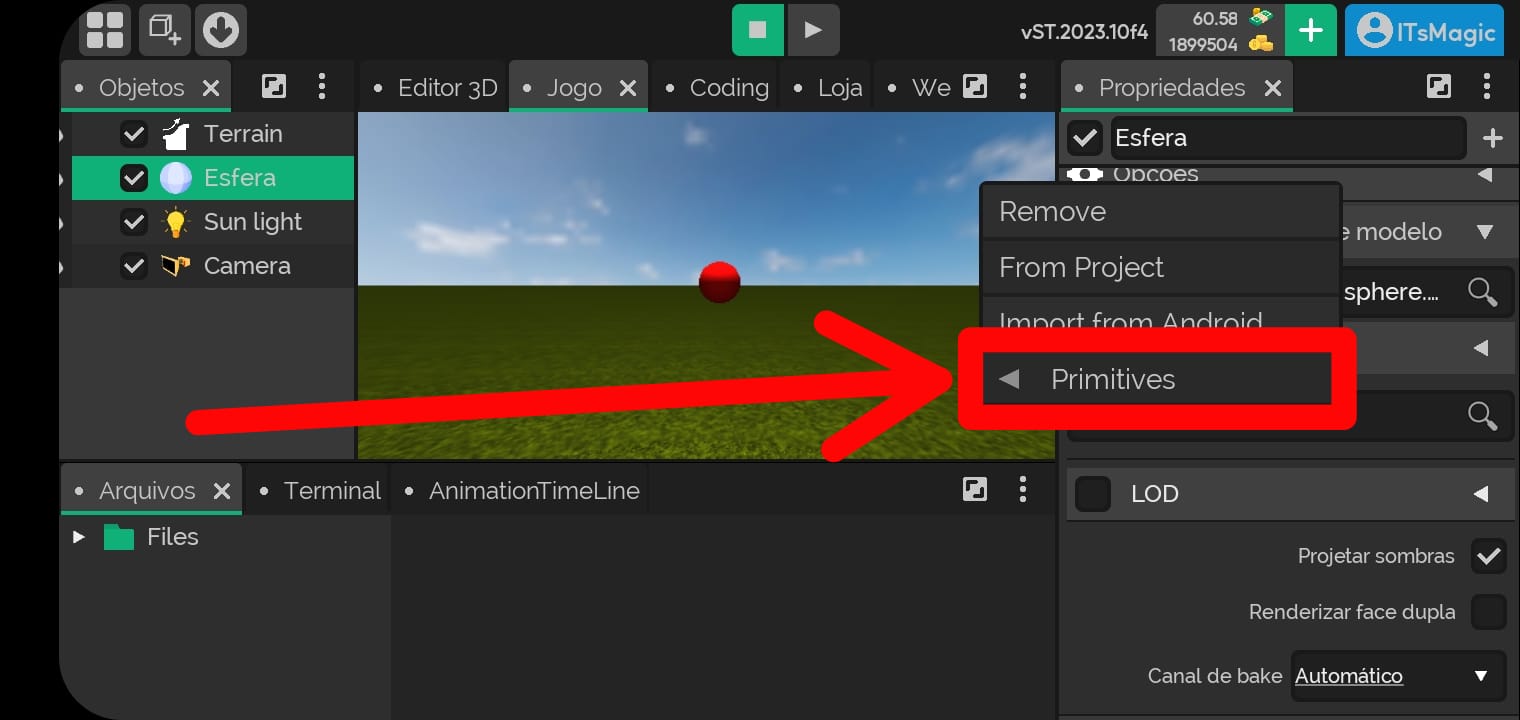
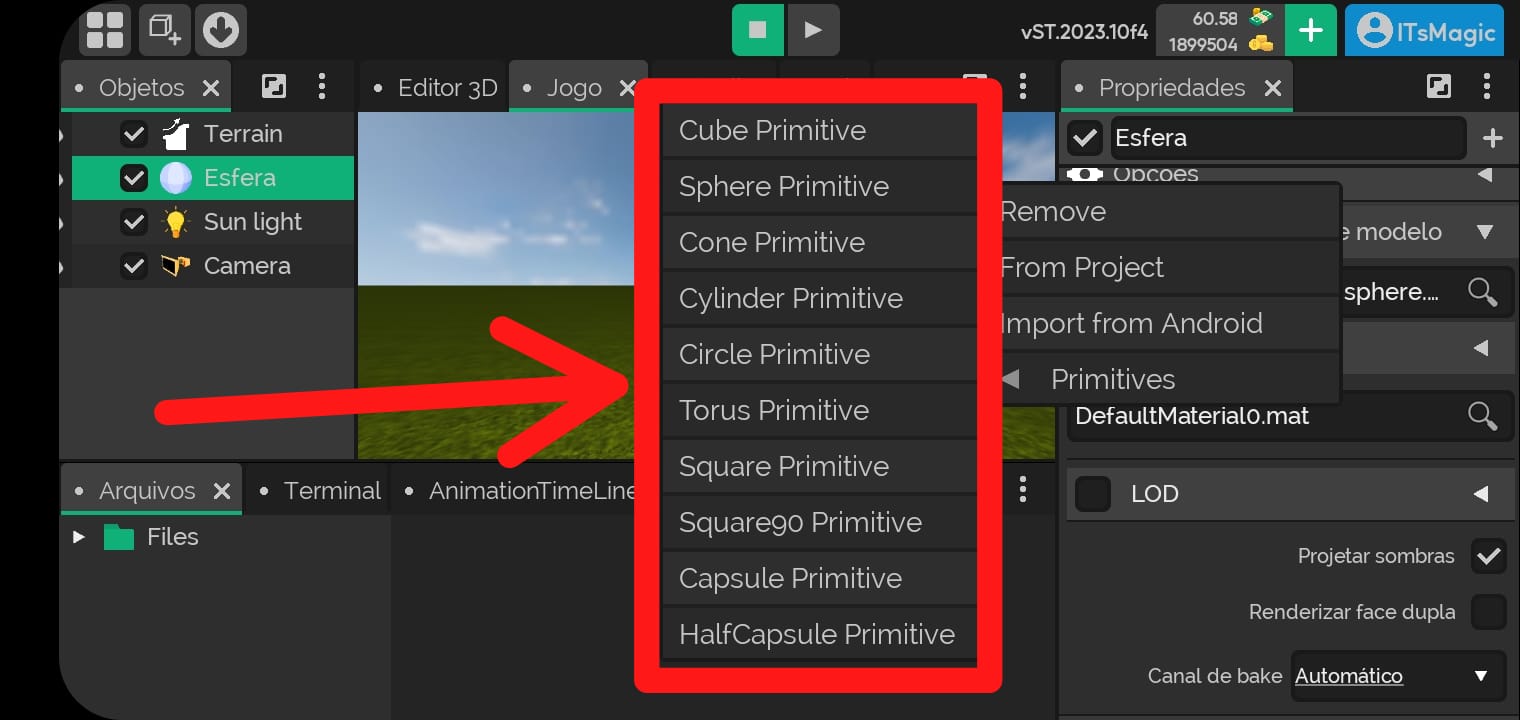
Primitive objects
- They are models of primitive objects (base models, spheres, cubes, cylinders, among others)
⚠️ click and hold in the location indicated in the image below ⚠️
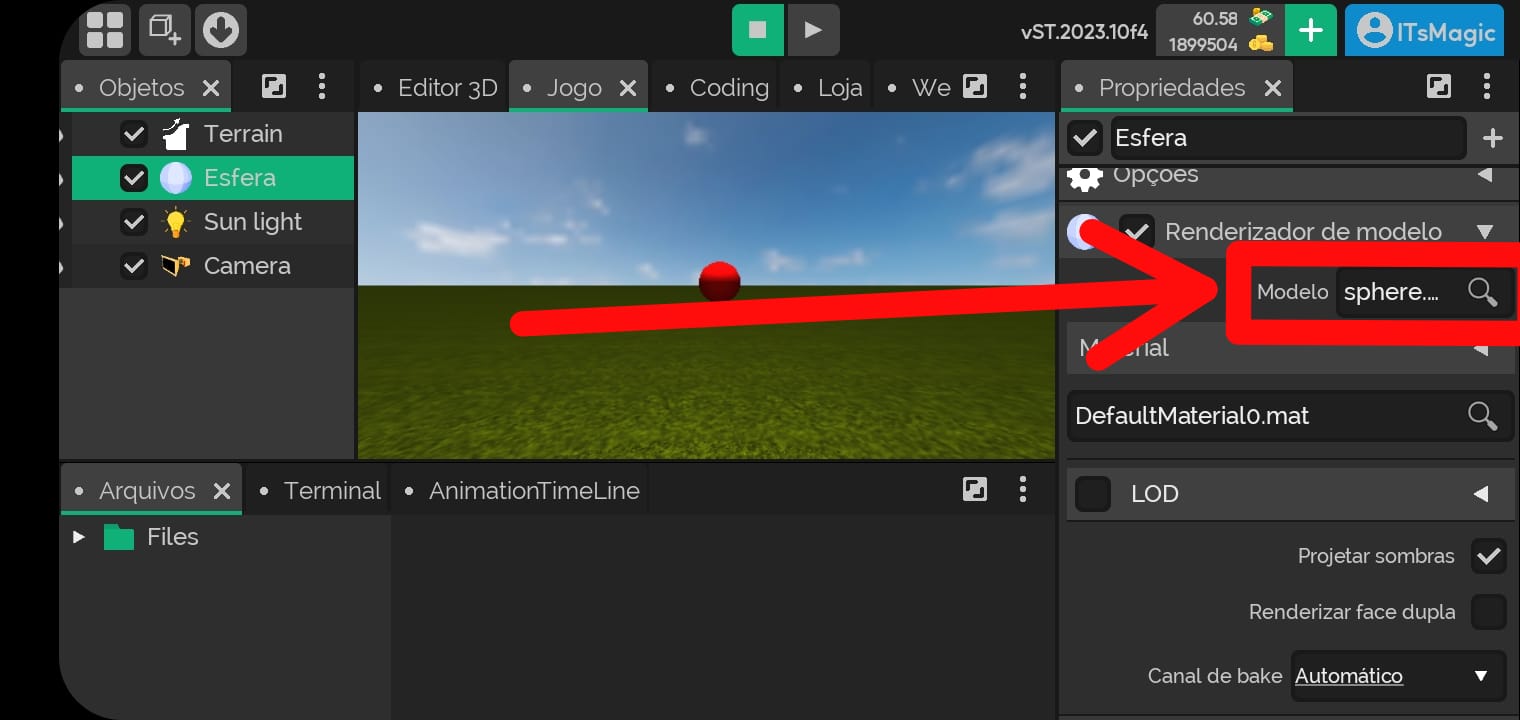
- In the example below we changed the model renderer from a sphere to a capsule.
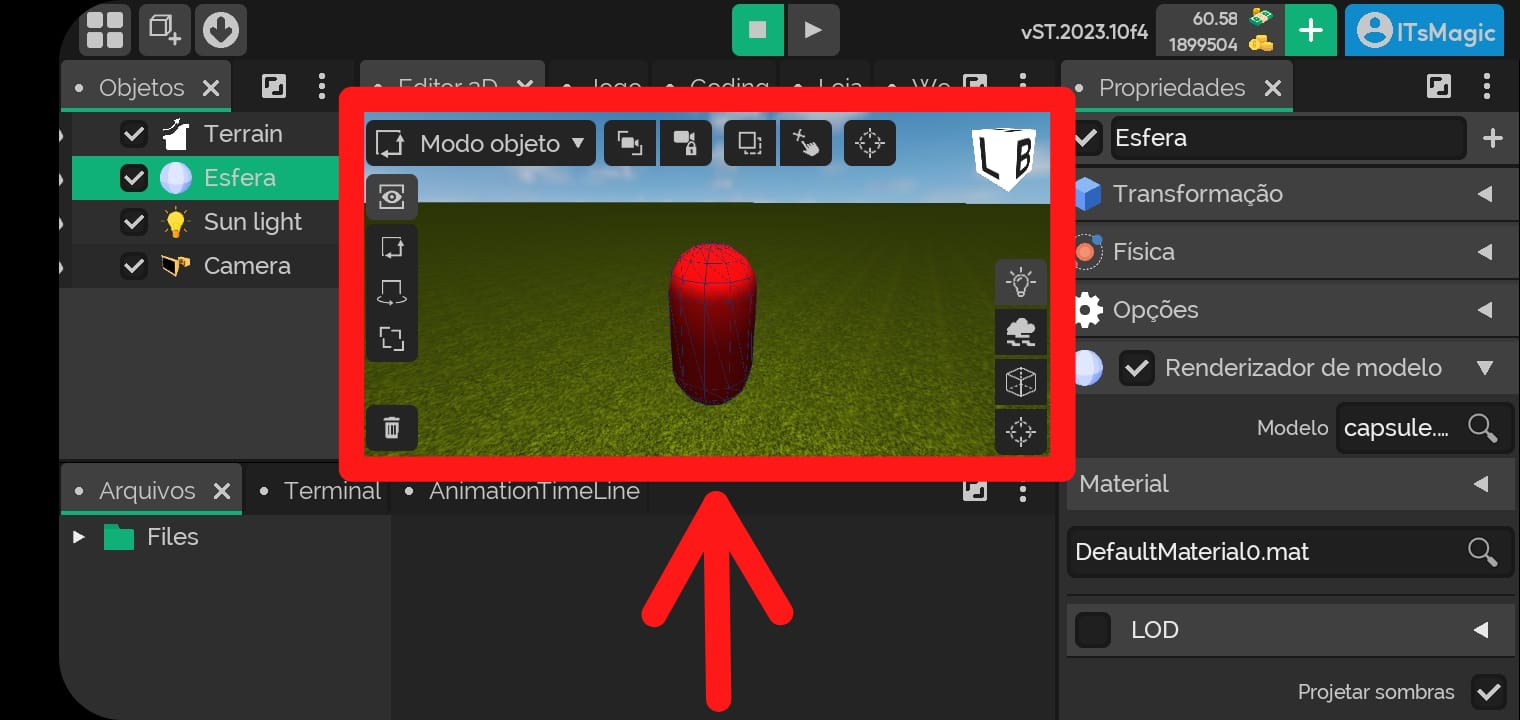
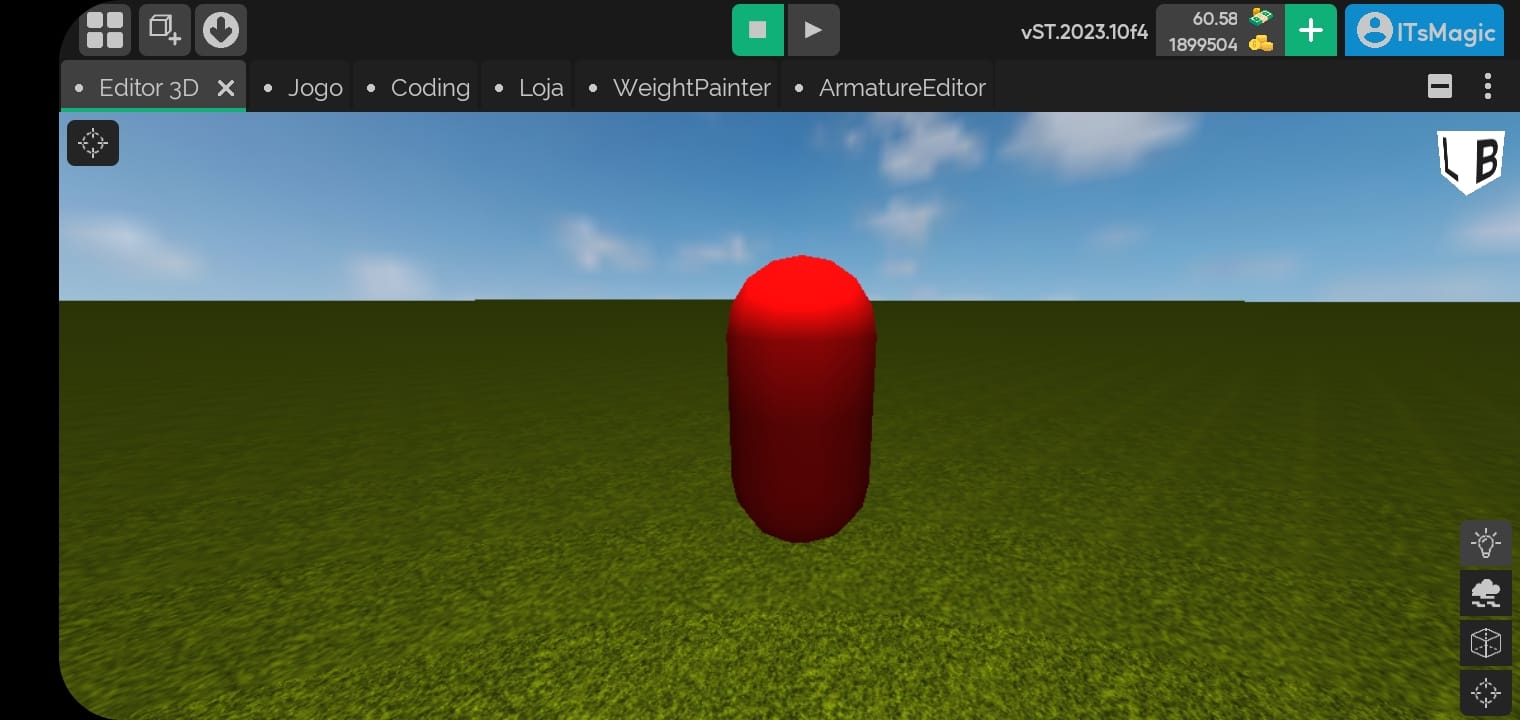
Material
- The Material is responsible for the properties of a shader (color, texture, transparency, among others) of the model renderer.
Shader
- Shaders are the properties of a material (color, texture, transparency, among others).
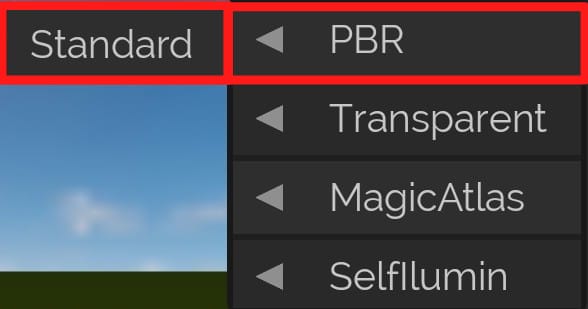
PBR
Standard
- The standard Material shader, used to render "real" objects such as "stones", "wood" and others.
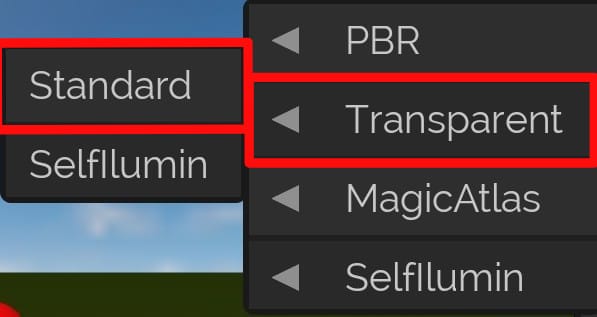
Transparent
Standard
- The default transparent shader, used to render "real" objects such as "stones", "wood" among others, however, in a transparent way.
SelfIlumin
- The shader used to render "real" objects such as "stones", "wood" among others, however, transparently and without any type of lighting.
MagicAtlas
Simple
- The shader used to render objects "lit" in a semi-transparent way.
SelfIlumin
DIF
- DIF (Draw in front), is the shader used to render objects that do not receive or interact with any type of light, however, it is rendered even if it is behind another object.
Simple
- The shader used to render objects that do not receive or interact with any type of light.
Receive light
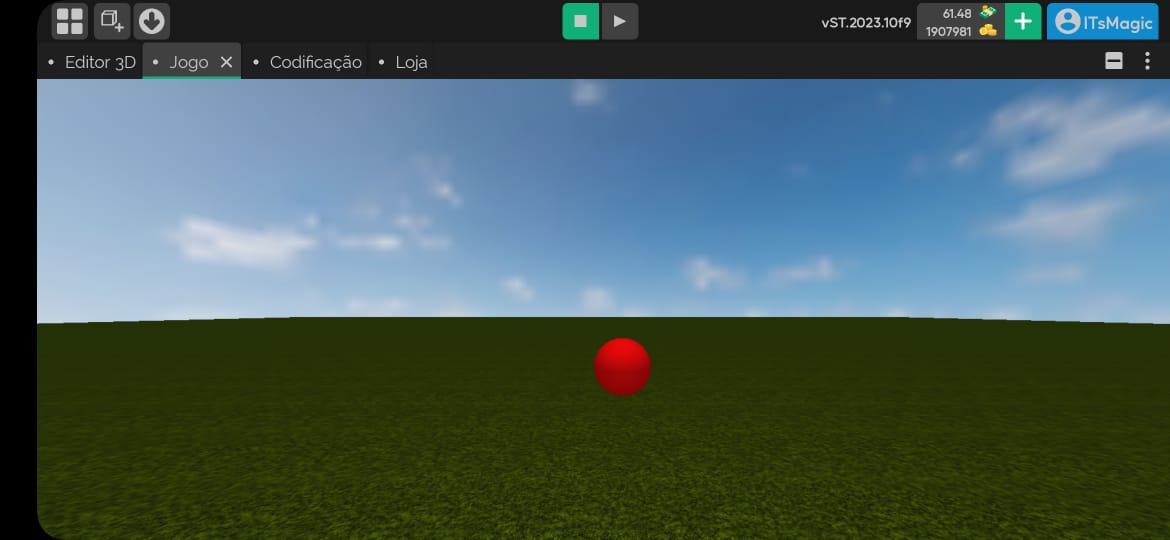
The property that defines whether the material will receive light or not.
Receive light activated
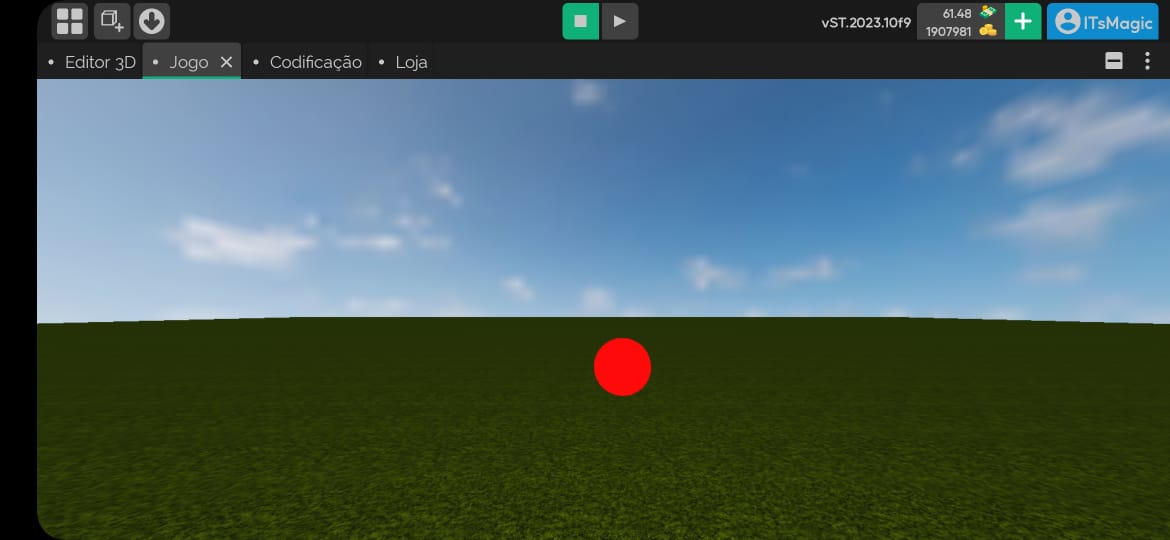
- Receive light disabled
AlphaCutout
- The cutting of transparency.
Diffuse
- The color of the Material.
Albedo
- The default texture of Material.
Normal
- Used to simulate additional surface details without increasing the geometric complexity of the model. It affects the way light interacts with the surface, giving the illusion of small details such as roughness or patterns.
Roughness
- Controls the apparent roughness or smoothness of a surface. Rougher surfaces reflect light more diffusely, while smoother surfaces have sharper reflections.
Specular
- Controls the intensity of specular reflections on a surface. Indicates areas that should be more reflective than others, adding realism to the appearance of materials.
Metallic
- Indicates which parts of an object are metallic and which are non-metallic. This influences the way light is reflected, especially on objects like metals that have more distinct reflections.
Ao
- Calculates the amount of light that each point on a surface receives, based on the proximity of other points. It is used to simulate darker areas in recesses or areas less exposed to light.
Height
- Used to create variations in the geometry of an object. It changes the position of vertices, adding height detail to the three-dimensional mesh.
Height intensity
- The intensity of the "height" texture.
DiscardEdges
- Defines whether texture edges will be discarded or not.
Emissive
- Emissive texture is used to add light emission to certain areas of an object, creating glow effects or standalone lighting in certain parts of the 3D model.
Alpha
- The transparency texture of Material.
MinimalAlphaIntensity
- The minimum intensity of the alpha.
UV Source
- Refers to two-dimensional texture coordinates that are assigned to each vertex of a 3D object. These coordinates are used to map a 2D image or texture onto the object's 3D surface.
Vertex
- Applies repeating Material textures according to the model's vertices.
World
- Applies repeating Material textures according to the size of the model in the world.
UV Size
UV
- The repetition of Material textures.
AlbedoTilling
- The repetition of the "albedo" texture in the model.
AlbedoOffset
- The displacement of the "albedo" texture in the model.
NormalTilling
- The repetition of the "normal" texture in the model.
NormalOffset
- The displacement of the "normal" texture in the model.
RoughnessTilling
- The repetition of the "roughness" texture in the model.
RoughnessOffset
- The displacement of the "roughness" texture in the model.
MetallicTilling
- The repetition of the "metallic" texture in the model.
MetallicOffset
- The displacement of the "metallic" texture in the model.
AoTilling
- The repetition of the "ao" texture in the model.
AoOffset
- The displacement of the "ao" texture in the model.
HeightTilling
- The repetition of the "height" texture in the model.
HeightOffset
- The displacement of the "height" texture in the model.
LOD
- LOD (Level of Detail) serves to balance visual quality and performance in 3D environments, automatically adjusting the level of detail of objects based on proximity to the viewer (Camera). This oENimizes resources, improving rendering efficiency in games and simulations, enabling a smoother user experience.
Start distance
- The initial distance that the LOD will be applied to.
End distance
- The final distance that the LOD will be applied to.
Levels
- The number of models that are generated with the number of reduced vertices.
Minimum quality
- The minimum quality of the model.
Aggressiveness
- The quality level of the model that is reduced with distance.
Cast shadows
- Defines whether the model's shadows will be cast or not.
Render dual face
- Defines whether the internal faces of the model will be rendered or not.
Bake channel
- Refers to the process of pre-calculating and storing lighting information in Material textures.
Automatic
- Automatically defines the bake channel.
Dynamic
- Generates the bake channel in real time.
Static
- Generates the bake channel upon scene loading.
Disabled
- Disables the generation of the bake channel.